

The claims that binaural beats will help memory or attention or relaxation seem a bit fuzzy to us, based on our results.” Feeling the beatįirst discovered in 1839, binaural beats didn’t hit the mainstream until 1973, when a Scientific American article brought them to the forefront. “The study is bringing some reality into the sensational claims about that. In both types of beats - binaural and monaural beats - the team did not observe a significant effect on mood or cognition.

“Compared to monaural beats, we observed less effect on the brain,” Dumas says. “We are not saying at all that there is no effect of binaural beats that’s still an open question,” Guillame Dumas, a researcher at the University of Paris, tells Inverse.īinaural beats do induce brain wave entrainment, or brain waves synchronizing to a rhythmic sonic stimulus, but not any better than normal beats. Binaural beats don’t affect the mind or body any more than monaural - normal or regular - beats, the new study, published Monday in the journal eNeuro, suggests.
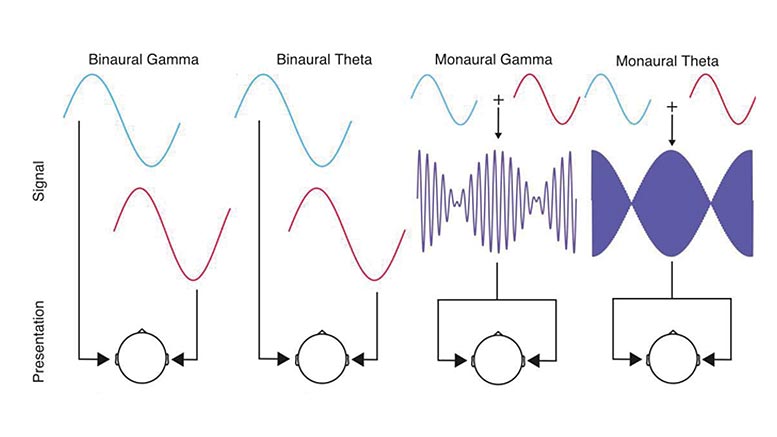
This strange auditory illusion is called a binaural beat, a phenomenon that’s been linked to stress relief, mood changes, pain modulation, and better sleep.īut new research puts these “sensational claims,” as one researcher puts it, under fire. You start to hear a third sound, a rhythmic beat that does not exist. When you hear two slightly mismatched sounds, an odd thing can happen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
